
Signs of Mold in Your House: Causes of Mold Growth and How to Prevent It
Mold is one of those silent problems that many homeowners don’t notice until it has already spread and caused damage. It thrives in damp, poorly ventilated areas and can grow on walls, ceilings, floors, furniture, and even inside HVAC systems. Left unchecked, mold not only damages your property but also creates serious health risks for you and your family. Understanding the early signs of mold, why it develops, and how to prevent it can save you from costly repairs and protect your indoor air quality.
In this article, we’ll walk through the signs of mold in your home, the main causes behind mold growth, its effects on health, and the best ways to prevent it.
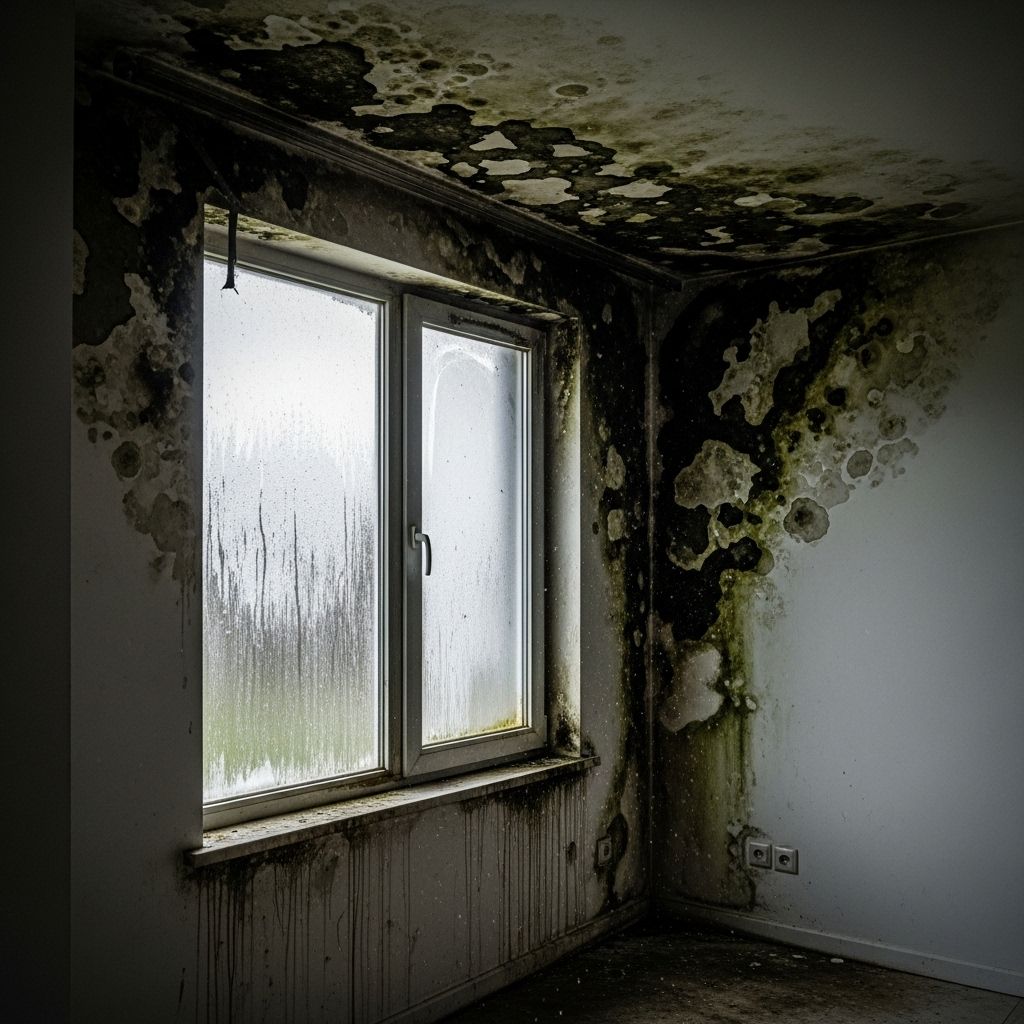

Signs of Mold in Your House
Mold isn’t always easy to spot. In many cases, it grows in hidden areas like behind drywall, under carpets, or inside air ducts. However, there are several clues that can help you identify a mold problem early:
Musty or Damp Odor
One of the earliest and most noticeable signs is a musty, earthy smell. Even if you can’t see mold, a persistent odor in certain rooms—especially basements, bathrooms, or laundry rooms—often indicates hidden mold growth.
Visible Discoloration on Walls
Mold appears in many forms: black spots, green patches, or white fuzzy growth. If you see unexplained stains or spots on walls, ceilings, or tiles, it could be mold rather than dirt.
Peeling Paint or Wallpaper
Moisture buildup behind walls often causes paint or wallpaper to peel, bubble, or crack. This is usually a sign of hidden mold colonies spreading inside the wall.
Dampness and Condensation
If you regularly notice condensation on windows, walls, or pipes, there’s likely excessive humidity in your home. This environment is perfect for mold to thrive.
Allergic Reactions or Respiratory Issues
Sometimes the first sign of mold is your health. Frequent sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, or worsening asthma indoors can indicate mold spores circulating in the air.
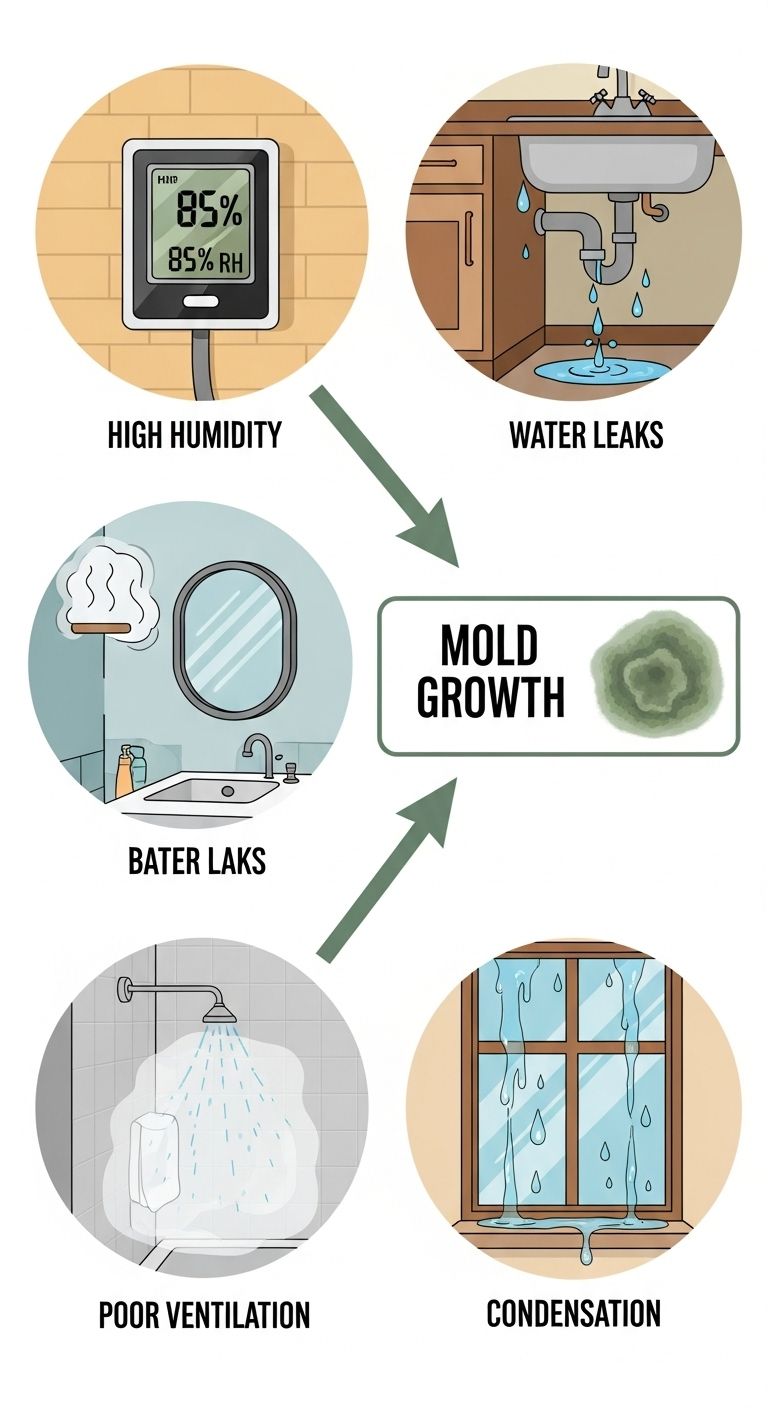
Causes of Mold Growth
Mold does not appear randomly—it needs certain conditions to grow. By understanding these causes, you can reduce the chances of mold invading your home.
1. Excess Moisture and Humidity
Mold thrives where there is constant dampness. Humidity levels above 60% create the perfect breeding ground. Bathrooms, basements, and kitchens are especially vulnerable.
2. Water Leaks
Leaky roofs, burst pipes, or plumbing issues introduce moisture that can go unnoticed for weeks. By the time you see visible damage, mold may already be spreading behind walls or under floors.
3. Poor Ventilation
Without proper air circulation, humidity builds up in rooms like attics, crawl spaces, and bathrooms. Stagnant air allows moisture to linger, which accelerates mold growth.
4. Flooding or Water Damage
Homes affected by flooding or storm damage are at high risk. Even after cleanup, moisture trapped in walls and floors can support mold growth for months.
5. Building Materials
Certain porous materials—like wood, drywall, and carpet—absorb and retain moisture. Once mold spores settle on these surfaces, they spread quickly.
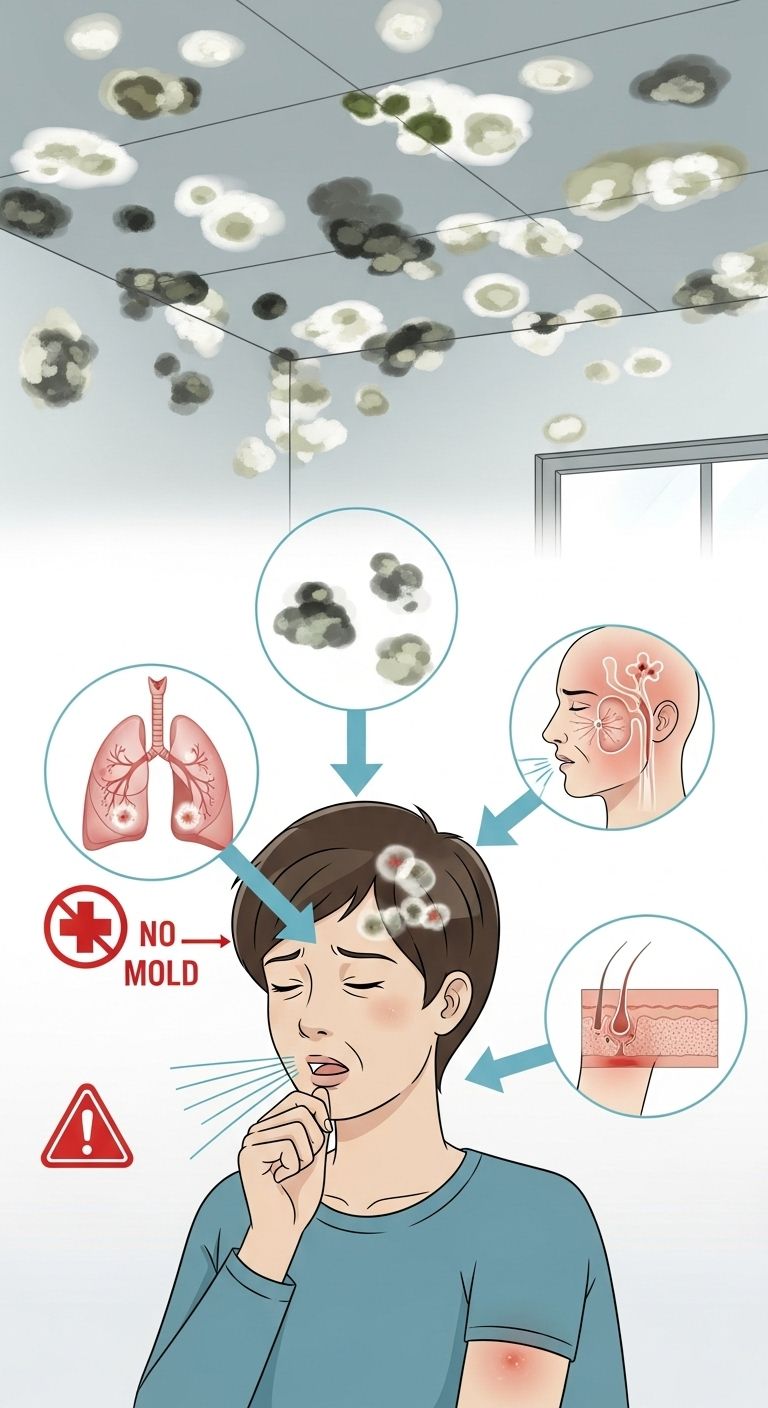
How Mold Affects Your Health
Mold isn’t just an eyesore—it has real consequences for your health. Mold spores are airborne, which means you can breathe them in without realizing it.
1. Allergic Reactions
For sensitive individuals, mold exposure can trigger symptoms similar to seasonal allergies: sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin irritation.
2. Asthma and Respiratory Problems
Mold is especially harmful to people with asthma or existing lung conditions. It can worsen asthma attacks, cause shortness of breath, and lead to chronic coughing.
3. Weakened Immune System
People with weakened immune systems—children, elderly, or those undergoing medical treatments—are at higher risk of infections caused by mold exposure.
4. Long-Term Effects
Prolonged exposure to certain types of mold, such as black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum), has been linked to serious health issues like chronic fatigue, headaches, and even neurological problems.
How to Prevent Mold Growth
Prevention is the key to protecting your home and health. The good news is, with proper maintenance and attention, mold growth can often be avoided.
- Control Indoor Humidity
Keep indoor humidity levels between 30–50%. Using dehumidifiers in damp areas like basements can drastically reduce the risk of mold.
- Improve Ventilation
Install exhaust fans in bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms. Make sure your HVAC system is cleaned regularly and allows proper airflow.
- Fix Leaks Promptly
Check your roof, plumbing, and basement for leaks. Even small drips can lead to large mold problems over time if ignored.
- Dry Wet Areas Quickly
After spills, floods, or heavy rain, dry the affected area within 24–48 hours. Mold begins growing quickly once moisture lingers.
- Use Mold-Resistant Materials
If you are remodeling or building, consider mold-resistant drywall, paints, and insulation to prevent future problems.
- Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Vacuum carpets, clean tiles, and scrub bathroom surfaces regularly. Prevent soap scum and moisture buildup that mold thrives on.
Conclusion
Mold is a common but preventable problem in homes. By recognizing the early signs of mold, understanding the causes of its growth, and taking proactive steps to improve ventilation, control moisture, and fix leaks, you can keep your home safe and healthy. Remember, mold isn’t just about property damage—it directly affects your health and well-being.
If you suspect mold in your home, don’t ignore it. Early action is the best way to protect your home, your health, and your peace of mind.

